Disorders of the Heel
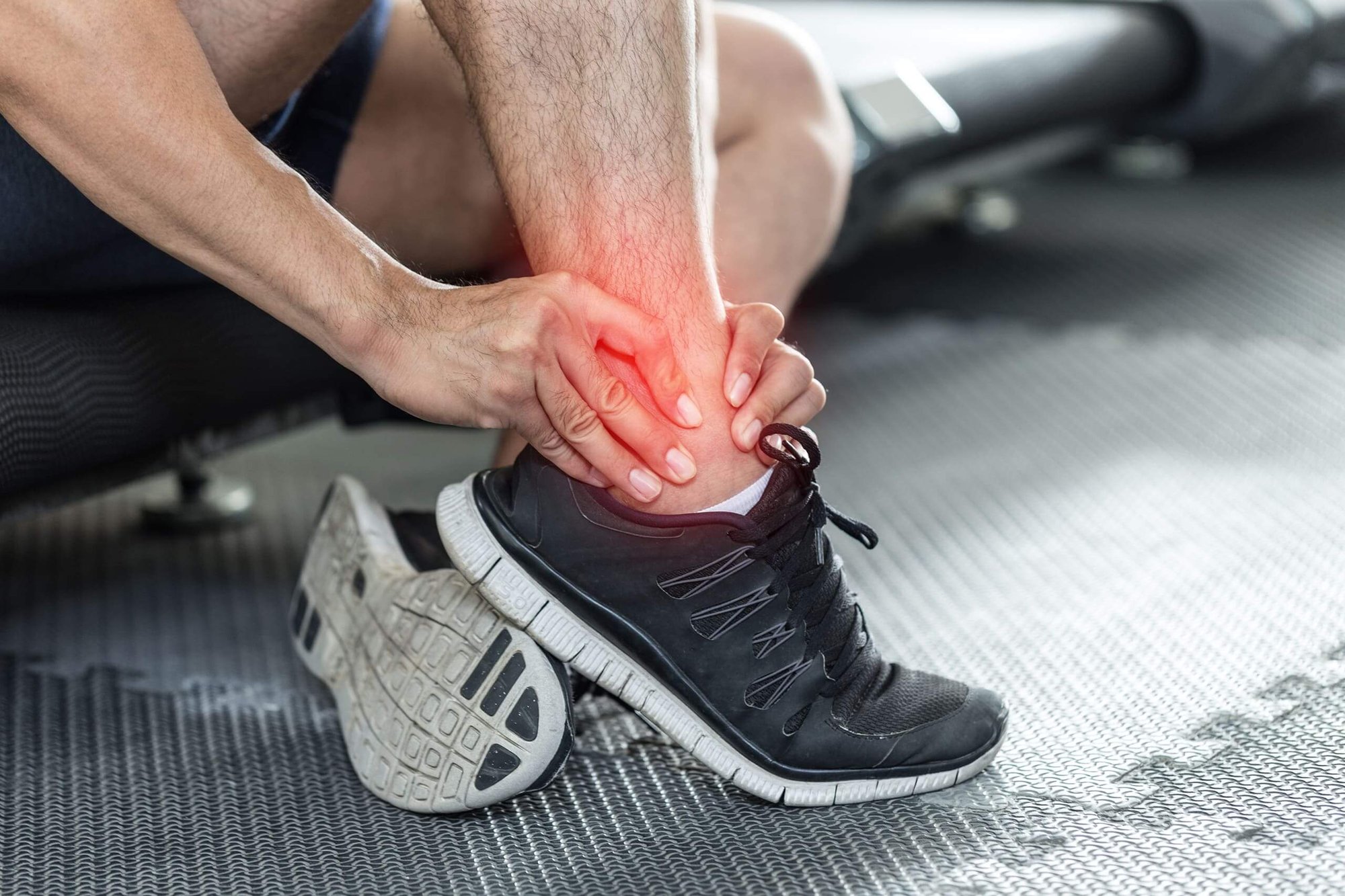
Heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, Haglund's exostosis, or achilles tendinitis may lead to chronic heel pain with subsequent impairment of gait. Caused by a mechanically induced chronic inflammation of the tendon-bone-interface or the tendon itself, this condition is addressed by anti inflammatory drugs, appropriate footwear, or extracorporal shock wave therapy.
Osteoarthritis
In the ankle-joint, severe osteoarthritis requires either stabilizing orthopaedic footwear, joint replacement, or an arthrodesis (fusion of the joint). Advanced stage osteoarthritis of the hind- and midfoot, as well as in the first metatarso-phalangeal joint, may equally be managed by arthrodesis.
In the lesser toes, resection arthroplasty, while more frequently undertaken to correct deformities, is also occasionally used in cases of osteoarthritis or rheumatic joint destruction.
Deformities of the Foot and Toes
Deformities of the Foot and Toes can be either congenital or acquired. While congenital club feet may be successfully treated by serial casting, achillotenotomy, and braces, according to the method of Ponseti, most cases of acquired foot deformities can be sufficiently treated with insoles, or, occasionally, custom made foot wear.
Major foot deformities due to direct trauma or neurological disorders may be managed either by joint preserving surgery, or corrective arthrodesis. Surgical correction can also be indicated in severe deformity of the first ray (the big toe), e.g. for hallux valgus, while rarely necessary in its lesser counterparts.
Trauma
Fractures of the foot and ankle frequently require internal fixation, while less severe cases are amenable to conservative treatment, mostly with braces. The majority of ankle sprains can be managed with orthotic devices, but selected ligamentous injuries, such as in Lisfranc luxation, need to be addressed surgically.
Stress fractures are the result of repetitive loading, e.g. in prolonged hiking, and occur most frequently in the midfoot. In the absence of dislocation, conservative treatment is indicated. Traumatic rupture of the achilles tendon can be treated either surgically or conservatively, as applicable. In elderly patients, this tendon may also give way spontaneously.